Alzheimer’s mental decline can be headed off years in advance of the occurrence of symptoms with the use of vitamin C supplements but not with oranges or apples that are considered to be vitamin C-rich foods.
Don’t wait for your doctor or public health authorities to produce a vaccine or a drug to prevent the predicted tripling of Alzheimer’s disease from 4.7 to 13.8 million by the year 2050. The research community has already identified the initial step in the development of Alzheimer’s but is reluctant to make a public health pronouncement that would upset the current pharmaceutical drug paradigm that predominates in modern medicines (none of the five classes of approved drug for this brain disease address its cause).
Mounting evidence points to vitamin C as a preventive measure to head off this ongoing mental health catastrophe. Consumption of vitamin C-rich foods (example: oranges) won’t be effective. Dietary supplements would be needed and taken throughout the day to achieve optimal blood levels as this water-soluble nutrient is rapidly excreted.
The science building up to this “discovery” is as follows:
- Brain levels of vitamin C are higher than in other in other organs.
- Blood plasma levels of vitamin C are lower in Alzheimer’s patients than in healthy individuals
- Deficiencies in vitamin C are associated with mental decline.
- Smoking tobacco, which depletes vitamin C, is increases the risk for Alzheimer’s dementia,
- Supplemental vitamin C improves the behavior of laboratory animals genetically engineered to develop Alzheimer’s.
- Individuals who consume vitamin C supplements are at reduced risk for Alzheimer’s mental decline.
- Alzheimer’s patients have lower blood plasma and cerebrospinal fluid vitamin C levels despite adequate dietary intake.
- Repeated consumption of high-dose vitamin C to laboratory animals reduced beta amyloid plaque levels in the brain by 40.2% (hippocampus) to 57.9% (cortex) in the brain of laboratory animals. Low-dose vitamin C (just enough to prevent scurvy symptoms) was almost ineffective at preventing mental decline whereas doses 10-fold higher than the minimum requirement were demonstrably effective. However, it doesn’t matter whether people have a buildup of plaque in their brain or not, they still develop mental decline, says a recent study. Measurement of beta amyloid plaque should be abandoned in favor of vitamin C blood and cerebrospinal fluid levels to predict risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
Laboratory studies in rodents are not applicable to the human condition because lab mice internally synthesize vitamin C whereas humans, due to a universal gene mutation, do not. That is why a study where laboratory mice were genetically reengineered so they were unable to internally produce vitamin C was the most applicable to brain health in humans.
Initial step
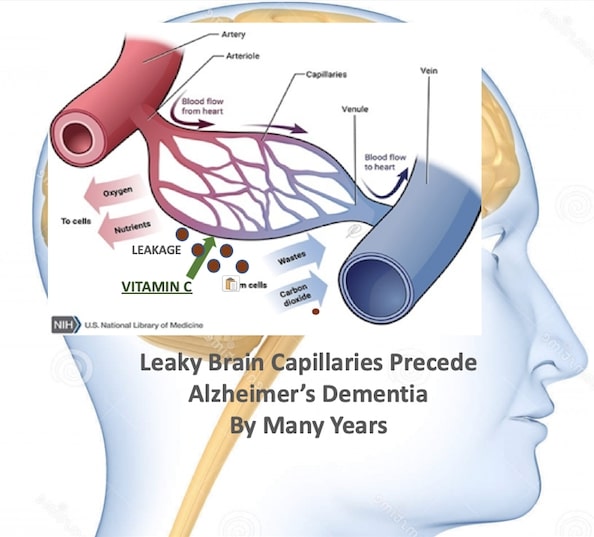
The initial step in the development of Alzheimer’s disease is leakage of blood from weak blood capillaries in the brain into surrounding tissues that occurs years before the appearance of clumps of proteins that destroy brain cells. This so-called breakdown of the blood-brain barrier is not addressed by any current drugs approved for the treatment of this disease. Vitamin C-nourished capillaries are stronger and less likely to leak into surrounding brain tissues.
It has been known since the 1940s that vitamin C strengthens blood capillaries. Capillaries are connectors between the red hoses (arteries) that carry oxygenated blood and nutrients to tissues and the blue hoses (vein) used to dispose of deoxygenated blood.
Prevention, can’t afford treatment
Worldwide Alzheimer’s cases are predicted to jump from 50 to 152 million over the same time. Annual cost of care is $818 billion/year now and will rise to $2 trillion, stifling world economies and in whispers, forcing health organizations to horrifically think of ways of covertly culling the demented population. That is what public health authorities are saying will happen “unless preventive measures are developed.”
For more than two decades it has been known in humans that that vitamin C is superior to other supplemental antioxidants (vitamin E, coenzyme Q10) in antioxidant protection in cerebrospinal fluid and it takes greater than dietary intake amounts of vitamin C (~110 milligrams/day) to elevate vitamin C levels in cerebrospinal fluid. Researchers have been calling for oral antioxidant supplementation to protect the human brain since 1997.
Don’t wait
The research community mindlessly continues to advise the public to wait until “drugs can be developed to help repair blood vessels and slow down or prevent the disease.” Preventive measures need to be practiced today to head off this predicted mental health disaster in the near future. Presumably, millions of vitamin C-deficient individuals already have leaky blood capillaries and are “cooking the disease.” Only diligent vitamin C supplement users are at reduced risk in the population. Given that vitamin C is a water-soluble nutrient that is rapidly excreted in urine flow, repeated doses (500 mg) every 4-6 hours are required to effectively prevent this devastating disease.
Blood plasma levels of vitamin C do not reliably predict future onset of Alzheimer’s disease because a blood test only reveals recent consumption and levels of vitamin C in the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the brain need to be much higher than in blood plasma to maintain brain health.
Other accompanying nutrients such as zinc, resveratrol and rice bran IP6 may synergistically reduce toxic metals (aluminum, copper) that also play a destructive role in Alzheimer’s disease.
The concurrent introduction of a pill that would double vitamin C blood levelsthroughout the day and night without the need for dietary supplementation is a new development that may make it easier to achieve vitamin C levels 24/7. ####